Check out this article for all the key points of Six Sigma for your production process management and organizational efficiency. Create your own Six Sigma matrix by using the recommended diagram software.
Six Sigma Basic Definition
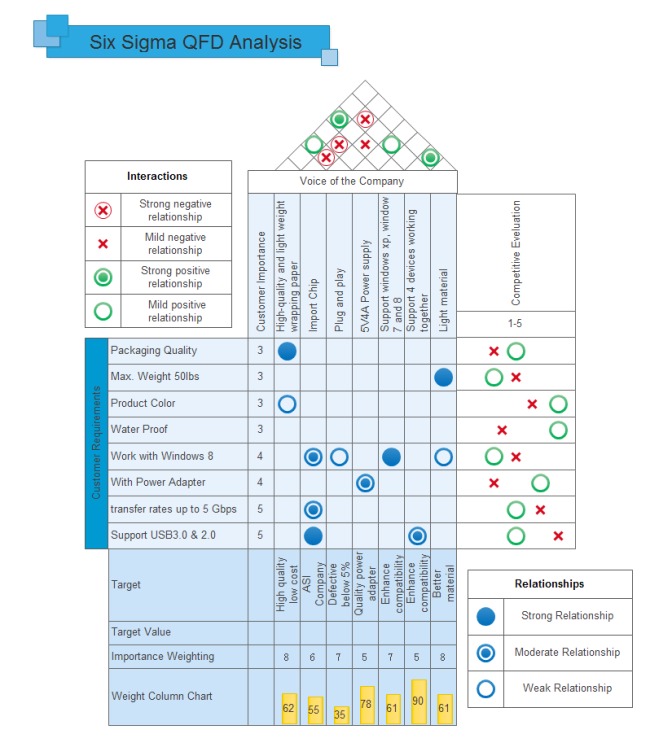
To be simple, Six Sigma is a disciplined approach for organizations to improve production process or service stability (e.g. the waiting time when different customers are calling a call center), reduce costs, eliminate defects, and deliver good customer service by analyzing statistical information. The standard metric requirement of Six Sigma is 3.4 defects per million opportunities, which means, for example, 3 or 4 low-quality products in one million produced. In order to apply the Six Sigma methodology, you need to have a deep understanding of cross-subjects including customer needs, data, statistical analysis, business management and so on. Below is a Six Sigma example in the software industry (click on it to enlarge the image).
More about the Advantages of Using Six Sigma Methodology
The methodology is mainly used to:
- Strengthen the understanding of project details, such as financial benefits, product advantages and features of organizational processes.
- Improve production processes metrics to speed up production cycle time.
- Help ensure long-term stability for further upgrades of products. This also helps organizations create a closed feedback loop for their products or services.
- Gain hands-on Information in Industrial project management, for example, in the Quality Management field.
Are there any Reminders of Using Six Sigma?
Everything has two sides, so does the Six Sigma methodology. Therefore, you should be careful with the following points when applying the approach to your project.
- For complex or large-scale projects, you may also consider some other analysis tools as a supplement.
- For the research and development of new products, especial those advanced technology ones, the use of Six Sigma may have a negative impact on exploring new factors.
- The use of Six Sigma can’t leave statistic analysis, but try not to rely too much on its statistic parts. The use of multiple regression techniques could increase the risk of making commonly unknown statistical errors.
Six Sigma Empirical Applications
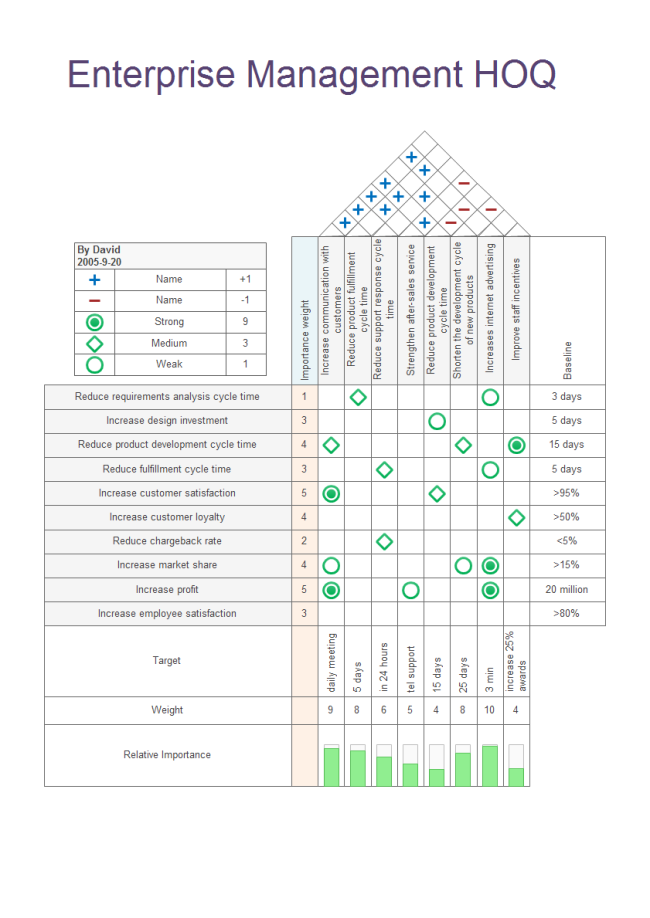
Six Sigma techniques so far have been applied in a wide range of industries and fields including aerospace, electronics, banking and finance, information technology, human resource management, marketing, and many more. Here is an example of enterprise management. Feel free to click on it to see insights.
Here we gonna look at more real-time cases:
Manufacturing
Around 2000, General Electric announced that Six Sigma methodology helped the organization saved millions of US dollars (according to GE annual report). Later, more international enterprises use the approach to waste reduction.
Construction
Six Sigma methodology can be used to control the building quality of international hotels or apartments, and to increase the production of heavy industrial materials such as steel. The construction time can also be reduced by using the methodology to prevent rework.
Finance Sector
Financial managers of many worldwide investment banks or financial institutions use the Six Sigma approach to improve the accuracy of cash allocations, reduce documentary credits defects and improve the weak financial streamline operations.
Logistics
Using Six Sigma can ensure good quality products be delivered in time by adjusting the schematic information for different delivery centers.
Public Sector
Six Sigma can also be applied to public services, such as frameworks, healthcare institutions, and roadway companies, to reduce equipment costs, alter the preparation process and provide safe services to the public.
How to Carry out a Six Sigma Analysis?
Although Six Sigma strategies may vary a lot between different firms because of their specific organizational cultures and business goals, there are three common methods for the use of a Six Sigma approach:
- DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control); It is an improvement system for existing processes.
- DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyze, Design and Verify); It is an improvement system used to develop new processes or products. The overall analysis process of DMADV is similar to DMAIC.
- LSS (Lean Six Sigma); It is a new methodology that integrates both Six Sigma principles and Lean concepts to decrease process variation and reduce waste. Lean, which also be called Lean Methods, is a series of techniques mainly used to reduce the waste generated from the flow of materials in an overall process. Sometimes, you may also need value stream mapping to gain more process details.
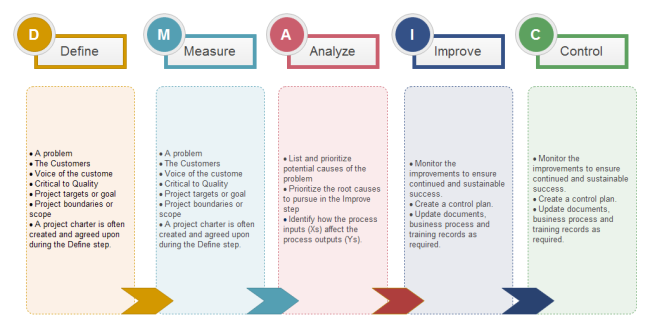
The most popular one among all these sub-category Six Sigma methodologies is DMAIC (as shown in the diagram below). Simply see the following steps to apply this approach and click on the image to check out more details.
Step 1: Define Your System
Your team should first draft a problem statement with clear and full details, for example, the quality requirement etc. Then you should define a clear project scope to keep the whole team focused on important issues. Next, you should identify project resources by assigning team members to different tasks. Finally, you should also develop a project plan with information such as in what way the project will be finished.
Step 2: Measure of Key Factors
Now, your team should completely analyze the current state of the project and creates a baseline for the system by developing detailed process maps and data collection plans (what, how often, and how many etc.). It is better to collect your datasets on process performance over a certain period of time and then recheck your data sets.
Step 3: Analyze the Gained Data to Find out Root Causes
You can do this step by using scatter plots and statistical models to identify and determine all possible root causes of the problem. Here, a fishbone diagram with a series of sub-branches (man, material, method, machine, measurement, and environment) is a good analysis tool for you.
Step 4: Improve the Current Process
It is time to improve your current process according to your data analysis by using techniques, such as brainstorming and risk-checking.
Step 5: Control and Monitor the Future State Processes
You should do this on a regular basis to ensure that any mistakes are corrected and the desired quality level is obtained. Next, update the process documentation with any changes due to the improvements. Also, make sure that all staffs related to the process understand the changes to the system.
Read More: